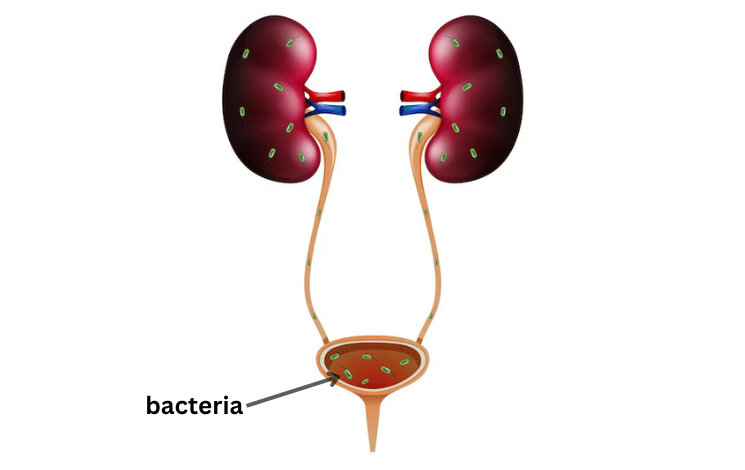
How do Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) form?
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) form when harmful bacteria enter the urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, and kidneys. These bacteria, often from the digestive system, can get into the urinary tract through the urethra. Once inside, they start multiplying and cause an infection. This leads to symptoms like a frequent urge to urinate, burning during urination, and discomfort in the lower abdomen. UTIs are more common in women due to their shorter urethra and can also result from factors like improper hygiene, sexual activity, or urinary retention. Treating UTIs usually involves antibiotics to clear the infection and relieve symptoms.
How To Prevent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) ?
To prevent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs), maintain good hygiene by wiping from front to back after using the toilet, drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria, urinate regularly to prevent bacterial buildup, empty your bladder before and after sexual activity, wear breathable cotton underwear, avoid harsh soaps and irritants, and consider incorporating cranberry products or probiotics into your diet. Additionally, promote healthy bathroom habits in children, avoid delayed urination, and seek medical attention promptly if you experience symptoms of a UTI.
Causes
- Bacteria entering the urinary tract
- E. coli bacteria from the digestive system
- Shorter urethra in women
- Sexual activity introducing bacteria
- Urinary retention (incomplete bladder emptying)
Symptoms
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Burning sensation during urination
- Passing small amounts of urine frequently
- Cloudy, bloody, or strong-smelling urine
- Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back
- Feeling tired or shaky
- Fever or chills (in severe cases)
Diagnosis
Sometimes a UTI will go away on its own. Most people will need antibiotics. Some people may be prescribed a 'delayed antibiotic', meaning they'll be asked only to use it if their symptoms don't go away after a certain amount of time.

Doctors

Homoeopathy
Dr. Pranav patel
Treatment
The usual treatment of bladder infection includes a course of antibiotics. The typical drug options are nitrofurantoin , trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (sample brand name: Bactrim), and fosfomycin